Knee Injuries
What is Knee Injuries
Knee pain can occur for many reasons, most commonly because of overuse, injuries or arthritis. You can experience knee pain at any age, but older people are more likely to develop it due to degeneration of the joint, a condition known as osteoarthritis.
Depending on what’s causing your pain, you may feel better with rest, anti-inflammatory medication and ice. If you have a more severe injury, you may need a procedure or a surgery.
Many knee injuries can be successfully treated with simple measures, such as bracing and rehabilitation exercises. Other injuries may require surgery to correct.
What Else Can Cause Knee Pain?
Bursitis. A bursa is a sac that holds a small amount of fluid that’s under the skin above your joint. It helps prevent friction when the joint moves. Overuse, falls, or repeated bending and kneeling can irritate the bursa on top of your kneecap.
Dislocated kneecap. This means that your kneecap slides out of position, causing knee pain and swelling. Your doctor may call this “patellar dislocation.”
Treatment of Knee Injuries
When you are first injured, the RICE protocol can help speed your recovery:
- Rest. Avoid putting weight on the painful knee.
- Ice. use cold packs for 20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Do not apply ice directly on the skin.
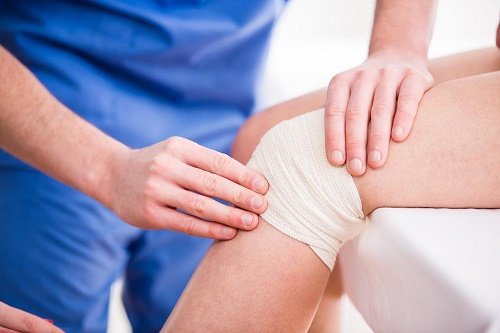
- Compression. Lightly wrap the injured area in a soft bandage or ace wrap.
- Elevation. To reduce swelling, elevate the injury higher than your heart while resting.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Many knee injuries can be treated with simple measures, such as:
Immobilization. Your doctor may recommend a brace to prevent your knee from moving.
Surgical Treatment
Many fractures and injuries around the knee require surgery to fully restore function to your leg.In some cases such as for many ACL tears surgery can be done arthroscopically using miniature instruments and small incisions.
Diagnosis
During the physical exam, your doctor is likely to:
- Inspect your knee for swelling, pain, tenderness, warmth and visible bruising
- Check to see how far you can move your lower leg in different directions
- Push on or pull the joint to evaluate the integrity of the structures in your knee
