Sprains & Strains
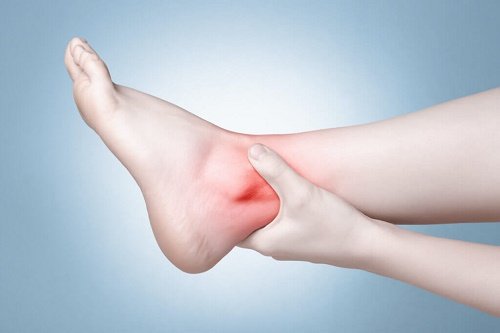
What is Sprains & Strains
Sprains and strains cause pain and loss of range of motion. They force employees to miss work and athletes to take time off from their sport.
Many sprains and strains heal on their own, with rest. But some need surgery or physical therapy to help rehab and prevent future injuries.
Sprains and strains both refer to damage to the soft tissues in the body, including ligaments, tendons, and muscles.
They are common injuries that share some symptoms but affect different body parts. People can often treat sprains and strains at home.
Symptoms of a Sprain
Sprains can happen when a joint twists in a weird position or bends too far. For example, an ankle sprain occurs because your ankle has twisted, and the ligaments attached around that joint stretch too much.
Symptoms of a sprain include:
- Swelling and tenderness of the joint.
- Bruising.
- Stiffness.
Symptoms of a Strain (muscle tear)
Symptoms of a strain may include:
- Sudden muscle pain, often from a certain movement or injury.
- Muscle spasm.
- Muscle that’s sore to the touch.
- Pain that may ease with rest.
- Muscle weakness.
Causes of Sprains
The most common causes of sprains are falling, twisting, or experiencing trauma to the joint. These types of injuries may cause the joint to move out of its normal range of movement, tearing or stretching the ligament as this happens.
Situations that may result in a sprain include:
- walking or running on an uneven surface
- twisting or pivoting suddenly
- falling and landing on the wrist or hand
- playing racquet sports
- injuries from contact sports
Causes of Strains
Strains may occur suddenly (acute) or develop slowly over time (chronic).
Causes of acute strains include:
- lifting a heavy object
- running, jumping, or throwing
- slipping or falling
Treatments
- Rest: Stop any exercise or physical activities and avoid putting any weight on the affected limb.
- Ice: Apply ice to the injury for up to 20 minutes every 2 to 3 hours. People can use bags of frozen vegetables if they do not have ice packs.
- Compression: To help reduce swelling, a person can wrap the affected area with a bandage or trainer’s tape. Loosen the wrap if the area gets numb or if the pain increases.
- Elevation: Keep the injured area raised above chest level if possible.
Preventation
- Strengthening muscles around joints: Regular conditioning and stability exercises can build a strong skeletal framework and help prevent injuries.
- Warm up properly before exercise: Warming up the muscles increases their range of movement and helps to avoid trauma and tears to connective tissue.
- Wear appropriate footwear: Shoes with proper support can help to protect the ankle and knee joints.
- Be aware of your environment: Watching out for slippery or uneven surfaces, or obstacles that may cause an accident, can help prevent injuries.
- Take breaks: Sitting or standing in one position for too long or performing repetitive actions can put undue strain on the muscles.
